- Homepage
- About Us
- Products
- Hi-Rel Fuses
- Hi-Rel Ferrite Chips
- Tin Whisker Mitigation
- Hi-Reliability Chip Resistors
- HRRAS Series Hi-Reliability High Power Anti-Surge Resistor
- HRRACX Series Hi-Reliability Chip Resistor Array - Convex
- HRRACV Series Hi-Reliability Chip Resistor Array - Concave
- HRRCS Series Hi-Reliability Metal Foil, Current Sensing Resistor
- HRRHS Series Hi-Reliability Ultra-High Power Anti-Surge Resistor
- FAQ
- Contact Us
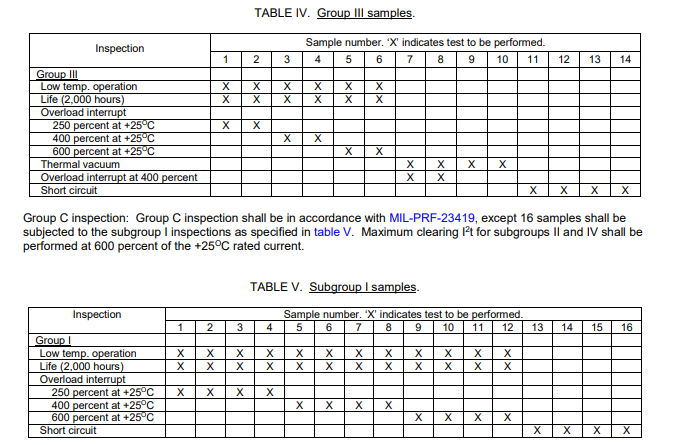
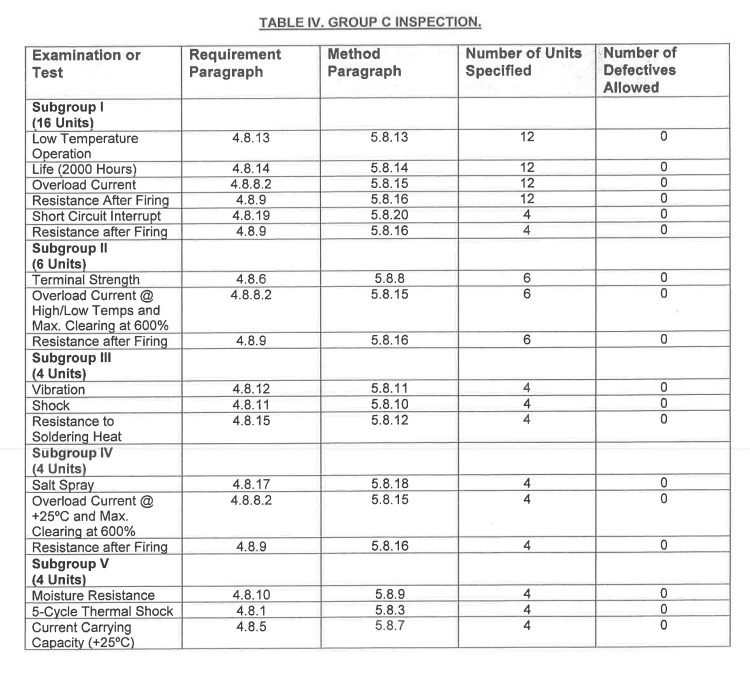
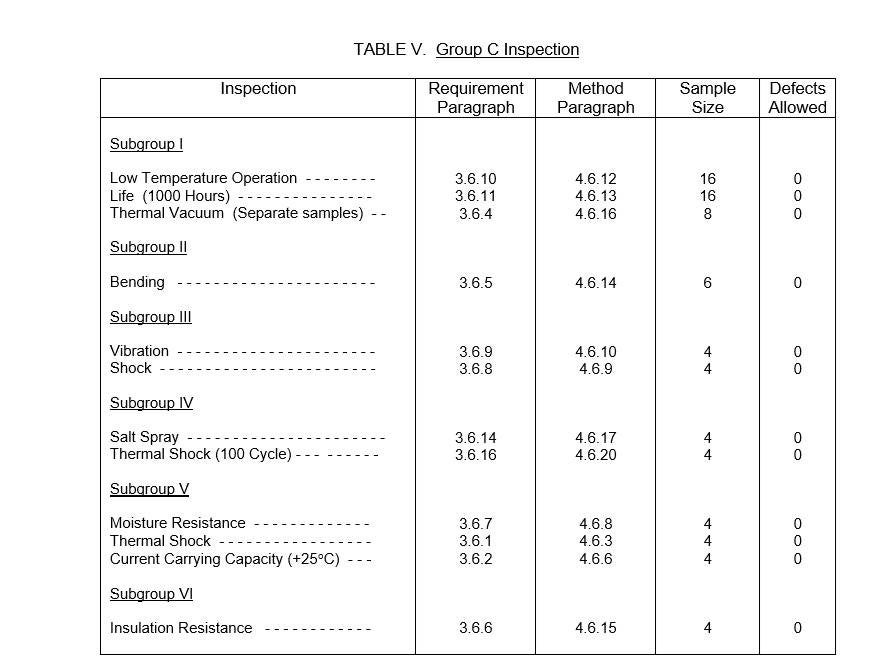
Home » FAQ